|
cvs.gedasymbols.org/djgpp/doc/dpmi/api/310507.html
|
search
|
Int 31H Function 0507H
Set Page Attributes
![[1.0]](../1.0.gif)
Sets the attributes of one or more pages within a linear memory block
previously allocated with Int 31H Function
0504H. This function can be used to change a committed page or a
mapped page to an uncommitted page, change an uncommitted page or a
mapped page to a committed page, or modify the read/write bit and
optionally the accessed and dirty bits on a committed or mapped
page.
Call With
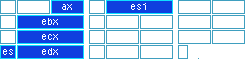
AX = 0507H
ESI = memory block handle
EBX = offset within memory block of page(s) whose
attributes are to be modified
ECX = number of pages
ES:EDX = selector:offset of a buffer containing page
attributes, 1 word (16-bits) per page (see Note)
Returns
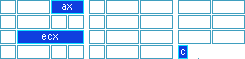
if function successful
Carry flag = clear
if function unsuccessful
Carry flag = set
AX = error code
| 8001H | unsupported function (16-bit host) |
| 8002H | invalid state (page in wrong state for request) |
| 8013H | physical memory unavailable |
| 8014H | backing store unavailable |
| 8021H | invalid value (illegal request in bits
0-2 of one or more page attribute words) |
| 8023H | invalid handle (in ESI) |
| 8025H | invalid linear address (specified range
is not within specified block) |
ECX = number of pages that have been set
Notes
- A DPMI 1.0 host that is 16-bit only will not support this
function.
- A 16-bit client of a 32-bit DPMI 1.0 host can use this
function.
- If EBX is not aligned, it will be rounded down to the next lower
page boundary.
- An uncommitted page can be created from:
- a committed page, by releasing the physical memory or backing
store allocated to the page;
- a mapped page, by marking it uncommitted; or an uncommitted page,
by doing nothing.
- A committed page can be created from:
- an uncommitted page or mapped page, by allocating physical memory
or backing store (with undefined, or zero-filled contents) for the
page; or
- a committed page, by doing nothing (page contents unmodified).
- The attribute word (16-bits) specified for a page has the
following format (bits 3-6 are only relevant if page is being created
committed or its attributes are being modified, i.e. the value in bits
0-2 of the page attribute is 1 or 3):
| Bits | Significance |
|---|
| 0-2 | page type (0-7) |
| Value | Meaning |
|---|
| 0 | create page uncommitted |
| 1 | create page committed |
| 2 | not allowed |
| 3 | modify attributes without changing page type |
| 4-7 | not allowed |
| 3 | 0 = page is read-only |
| 1 = page is read/write |
| 4 | 0 = don't modify accessed/dirty bits for page |
| 1 = set accessed/dirty bits as specified in bits 5-6 |
| 5 | 0 = mark page as not accessed (if bit 4=1) |
| 1 = mark page as accessed (if bit 4=1) |
| 6 | 0 = mark page as not dirty (if bit 4=1) |
| 1 = mark page as dirty (if bit 4=1) |
| 7-15 | reserved, should be zero |
- This function, and the optional Map Device and Map Conventional
Memory functions (Int 31H Functions 0508H
and 0509H), are the only means of changing
the type of a page within an existing memory block.
- The page read/write bit, and optionally the accessed and dirty
bits, can be modified on an existing committed or mapped page, or on a
committed page when it is initially created from an uncommitted page
or a mapped page. However, the accessed and dirty bits are ignored if
the host does not support the Page Accessed/Dirty capability. See Int 31H Function 0401H.
- Visible page faults (page faults that can be serviced by a
client-installed exception handler) can only occur for uncommitted
pages or read-only pages (for definitions of transparent page fault
and visible page fault, see Appendix A: Glossary).

